By GREGORY GONDWE and GERALD IMRAY
BLANTYRE, Malawi (AP) — Malawi’s Vice President Saulos Chilima and nine other people died when the small military plane they were traveling in crashed in bad weather in a mountainous region in the north of the country, the president said Tuesday. Chilima was 51.
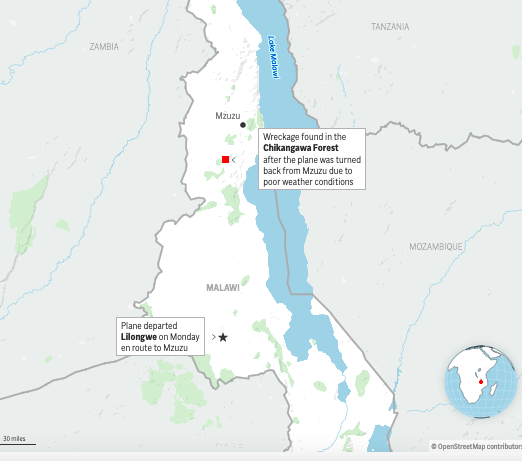
President Lazarus Chakwera announced that the wreckage of the plane that went missing Monday morning had been located after a search of more than 24 hours in thick forests and hilly terrain near the city of Mzuzu. He said the wreckage was found near a hill and the plane had been “completely destroyed,” with everyone killed on impact.
Malawi VP, 9 others killed in plane crash
Malawi’s vice president, Saulos Chilima, and nine other people died Monday when the small military plane they were traveling in crashed in bad weather in Malawi’s mountainous north.
It was a “terrible tragedy,” Chakwera said. “Words cannot describe how heartbreaking this is, and I can only imagine how much pain and anguish you all must be feeling.” He called Chilima “a good man, a devoted father and husband, a patriotic citizen who served his country with distinction and a formidable vice president.”
Chakwera said the victims’ remains were being brought to the southern African nation’s capital, Lilongwe. The seven passengers included members of Chilima’s staff and security detail along with former first lady Shanil Dzimbiri, the ex-wife of former President Bakili Muluzi. There were three crew members.
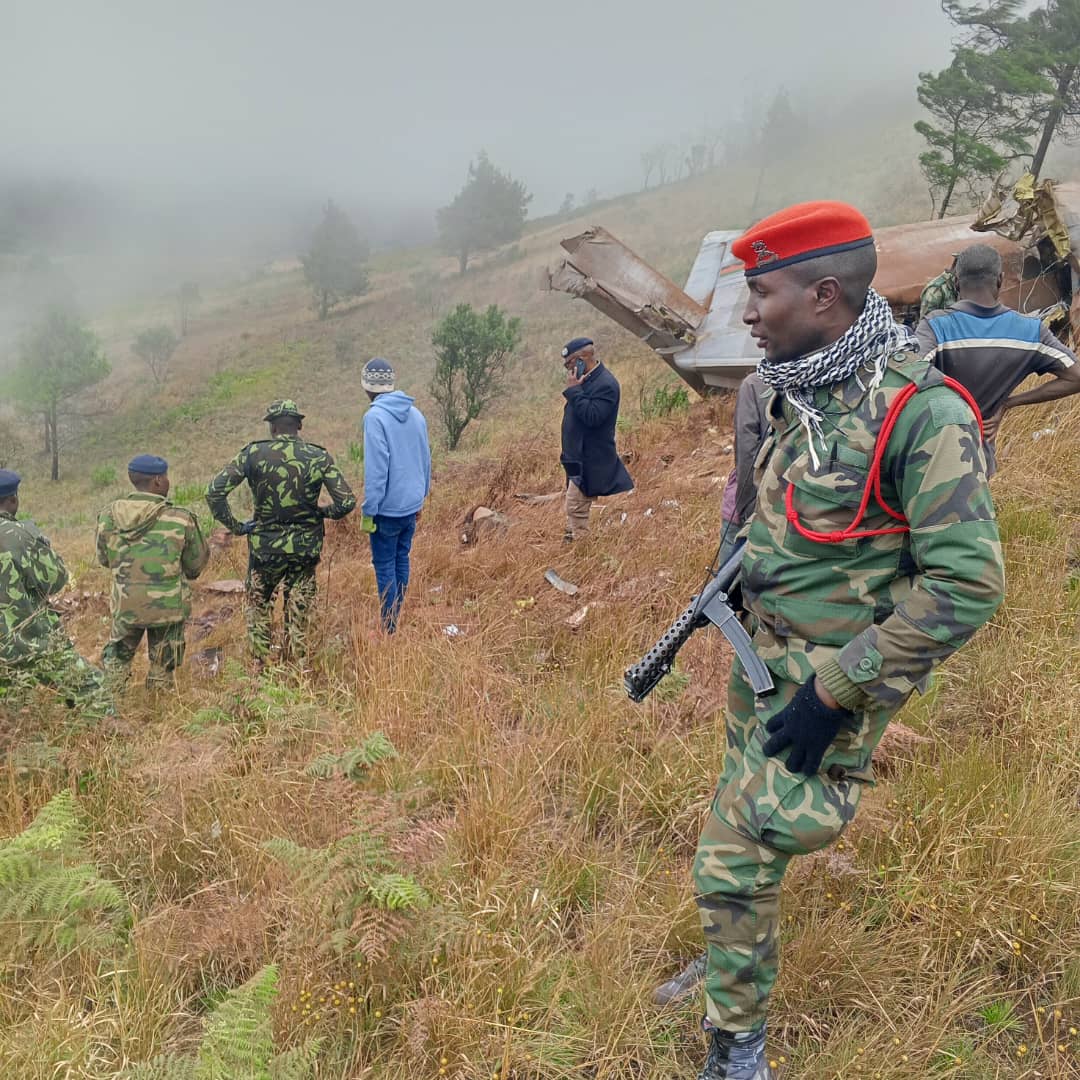

Hundreds of soldiers, police officers and forest rangers had searched for the plane since it went missing Monday at around 10 a.m. while making the 45-minute flight from Lilongwe to Mzuzu, around 370 kilometers (230 miles) to the north.
The group was traveling to attend the funeral of a former government minister. Air traffic controllers told the plane not to attempt a landing at Mzuzu’s airport because of bad weather and poor visibility and asked it to turn back to Lilongwe. Air traffic control then lost contact with the aircraft and it disappeared from radar.
Chakwera said the wreckage was found in the Chikangawa Forest south of Mzuzu. Images from the site showed thick fog over the hills and remnants of the plane in an open area near the tree line. The president described the aircraft as a small, propeller-driven plane operated by the Malawian armed forces.
Officials with Chilima’s United Transformation Movement political party — a party different from the president’s — criticized the government response as slow and said there was no transponder on the plane, concerning an aircraft carrying a high-level delegation.
Chilima and Chakwera had led Malawi under unusual circumstances. They both ran for president in 2019 as opposition candidates but teamed up to challenge election results in court over irregularities, and won. They then won the rerun of the election — the first time in Africa that a court-overturned election result resulted in a defeat for the incumbent president.
AP correspondent Charles de Ledesma reports Malawi’s vice president and 9 others have died in a plane crash.
Chilima had said Chakwera had agreed to step down after his first term and allow him to run for president in next year’s election as part of their alliance. However, Chakwera announced he would run for reelection, and there were signs of friction between the two.
Chilima also had recently faced corruption charges over allegations that he received money in return for influencing the awarding of government procurement contracts for the armed forces and the police. Prosecutors dropped the charges last month. He had denied the allegations.

Chilima had just returned from an official visit to South Korea on Sunday. He was in his second term as vice president after serving from 2014-2019 under former President Peter Mutharika.
The search for the plane prompted an international response. Chakwera said the U.S., the U.K., Norway and Israel had offered assistance and provided “specialized technologies.” The U.S. Embassy in Malawi said it had assisted and offered the use of a Department of Defense small C-12 plane. Malawi also asked neighbors Zambia and Tanzania if they could help.
Malawi, a country of around 21 million people, was ranked as the fourth poorest nation in the world by the World Bank in 2019.
Imray reported from Cape Town, South Africa. AP writer Farai Mutsaka contributed from Harare, Zimbabwe.














